Projection of the momentum p (t) in the observer's LNRF for a photon.... | Download Scientific Diagram

A particle of mass m, kinetic energy K and momentum p collision head on elastically with another - YouTube
23.A body is projected at angle 30 degree with the horizontal with momentum p. At its highest point the magnitude of momentum is
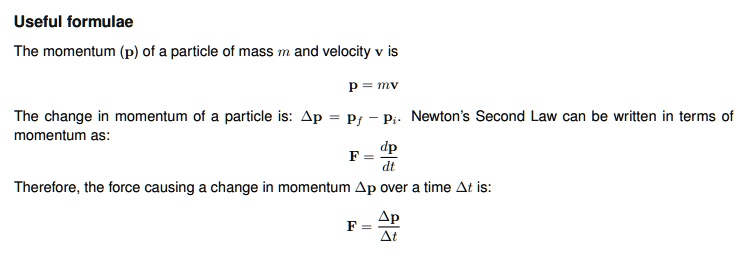
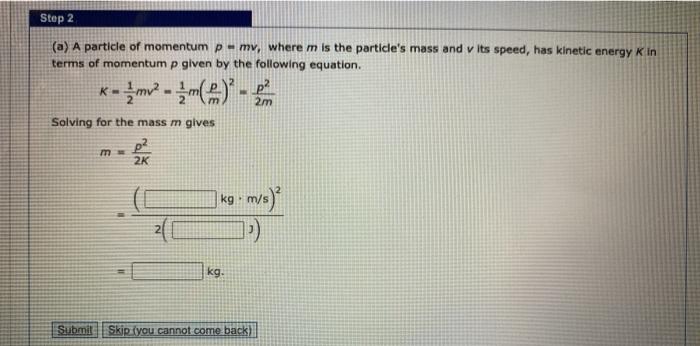
SOLVED: Useful formulae The momentum (p) of particle of mass mn and velocity p = MnV The change in momentum of a particle is: Ap = Pf Pi. Newtons Second Law can

A particle. has the position vector r = vec i - 2vec j + k and the linear momentum p = 2vec i - vec j + vec k . Its angular momentum about the origin is

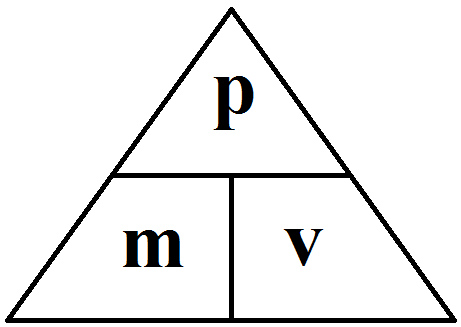
Momentum p = m v Momentum = mass * velocity momentum is directly proportional to an object's mass momentum is directly proportional to the object's velocity. - ppt download

Chapter 6 Momentum and Impulse - ppt video online download in 2023 | Physics notes, Learn physics, Physics lessons

Momentum Momentum is mass times velocity. Momentum is represented by p. p = mv Momentum is a vector quantity. The direction of momentum always matches. - ppt download

The linear momentum P of a body varies with time and is given by the equation P=x+yt2, where x and y - YouTube

Linear Momentum. Linear Momentum (p) Product of mass and velocity Equation p = mv Vector quantity with direction the same as v Unit kg-m/s. - ppt download